ITIL
ITIL, which stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a set of best practices and detailed guidelines for managing and optimizing IT service management (ITSM). ITIL aims to help organizations manage risk, strengthen customer relations, establish cost-effective practices, and build a stable IT environment that allows for growth, scale, and change.
Developed in the 1980s by the United Kingdom's Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (now part of the Office of Government Commerce), ITIL has undergone several revisions over the years, with the most recent version being ITIL 4, released in 2019. This latest version integrates modern technologies and methodologies such as Agile, DevOps, and Lean into traditional ITIL practices to better adapt to the changing IT landscape.
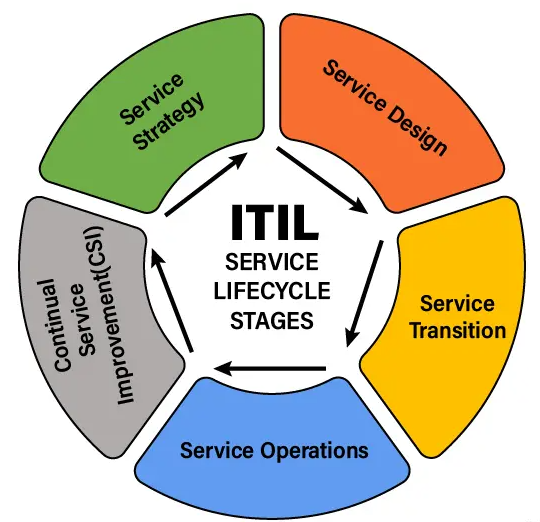
ITIL is structured around a service lifecycle, which includes five main stages:
- Service Strategy: This stage focuses on understanding organizational objectives and customer needs.
- Service Design: It involves designing IT services, processes, and other aspects of the service management effort.
- Service Transition: This stage manages changes to ensure that the transition is smooth and that service quality is maintained.
- Service Operation: It focuses on the day-to-day maintenance and operation of services.
- Continual Service Improvement: This stage aims to continuously improve the effectiveness and efficiency of IT processes and services.
Organizations use ITIL to improve efficiency and achieve predictable service levels, and many companies require their IT staff to be certified in ITIL.
What are the ITIL controls?
In the context of ITIL, "controls" refer to the policies, procedures, and practices that are put in place to ensure that IT services are managed effectively and efficiently. These controls are designed to help organizations achieve their service management goals while mitigating risks and ensuring compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
ITIL controls are part of the broader ITIL framework, which guides organizations in planning, delivering, operating, and controlling IT services aligned with business needs. The controls are embedded in various processes across the ITIL service lifecycle, including service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement. Here’s a more detailed look at how controls function within ITIL:
-
Governance and Compliance: ITIL controls help ensure that IT services are governed in line with organizational policies and legal requirements. This includes compliance with laws, regulations, and internal standards.
-
Risk Management: Controls are critical for identifying, assessing, and managing risks associated with IT services. This includes defining risk thresholds and implementing measures to mitigate risks.
-
Process Control: ITIL emphasizes the importance of well-defined processes for managing IT services. Controls are used to ensure that these processes are carried out consistently and effectively, and that they meet their intended outcomes. This includes checks and balances, process documentation, roles and responsibilities, and performance metrics.
-
Audit and Assurance: Controls facilitate auditing by providing clear criteria for what should be inspected and how processes should be executed. This helps in identifying non-conformities and areas for improvement.
-
Service Improvement: ITIL controls also support continual service improvement by providing mechanisms for measuring process performance and implementing improvements based on data and feedback.
Overall, ITIL controls are essential for establishing a disciplined approach to service management, ensuring that services are delivered in a way that supports business objectives and meets customer expectations. They help create a stable management environment capable of adapting to change and scaling operations in a controlled manner.
What are the benefits of ITIL?
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) offers a variety of benefits for organizations that adopt its framework. These benefits span across improving service delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction, and achieving operational efficiency. Here are some of the key advantages of implementing ITIL practices:
-
Improved Service Quality: ITIL provides a systematic approach to service management, which helps in delivering more reliable, consistent IT services. This improves the overall quality of service delivery by ensuring that services are designed, managed, and delivered according to defined and standardized processes.
-
Increased Efficiency: By standardizing processes and following best practices, ITIL helps organizations reduce waste and avoid rework. This leads to increased efficiency in the use of resources and capabilities, ultimately reducing costs and improving service turnaround time.
-
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: With ITIL, services are aligned more closely with current and future needs of the business and its customers. This focus on customer needs helps improve customer satisfaction by delivering services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
-
Better Risk Management: ITIL provides a structured approach to managing risks by identifying, assessing, and managing potential disruptions to service. This proactive risk management helps prevent incidents and ensures smoother, more reliable operations.
-
Stronger Alignment Between IT and Business: ITIL encourages the alignment of IT and business strategies, ensuring that IT processes and services support overarching business goals. This alignment increases the business value of IT investments and helps IT departments be viewed as strategic partners rather than just support functions.
-
Enhanced Ability to Manage Change: With its structured approach to service transition and change management, ITIL helps organizations manage changes more effectively, minimizing disruptions to services and reducing the risk of unplanned outages.
-
Improved Service Innovation and Development: ITIL's frameworks support continual service improvement and innovation by providing methodologies for feedback, assessment, and adaptation of services. This supports ongoing development and makes it easier for IT services to adapt to changing technology and market conditions.
-
Greater Visibility into IT Operations: By standardizing documentation, metrics, and reporting processes, ITIL increases the visibility of IT operations and performance. This greater transparency aids in decision-making and helps demonstrate the value of IT to business stakeholders.
-
Support for Compliance and Security Management: ITIL's frameworks include processes for ensuring that IT services comply with legal and regulatory requirements. This also extends to improving the organization's handling of data security within the IT service lifecycle.
Overall, the adoption of ITIL can lead to more efficient and effective IT service management, significantly contributing to the operational excellence and strategic development of an organization.
How to implement the ITIL?
Implementing ITIL in an organization involves a structured approach to integrate ITIL best practices into the management of IT services. The implementation process can be complex, requiring careful planning, training, and change management to ensure it aligns well with the organization’s goals and existing processes. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you understand how to successfully implement ITIL:
1. Assess Current Capabilities and Needs
- Conduct an Assessment: Start by assessing the current state of IT service management within your organization. Identify existing processes, capabilities, and areas of improvement.
- Identify Objectives: Define clear business and IT objectives that the ITIL implementation will support. This helps ensure alignment with business goals.
2. Obtain Commitment and Support
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders, including IT staff, management, and end-users. Their support and buy-in are crucial for the success of the implementation.
- Secure Executive Sponsorship: Gaining support from top management ensures the necessary resources and authority are available for the implementation.
3. Train and Certify Key Personnel
- Provide Training: Educate IT staff about ITIL principles, practices, and processes. Consider formal training and certification courses to build expertise.
- Develop an Internal Capability: Develop a team of ITIL-aware members who can champion the process within the organization.
4. Define the ITIL Roadmap
- Start Small: Choose a manageable segment of ITIL that closely aligns with your organization’s immediate needs, such as Incident Management or Change Management.
- Plan Phases: Implement ITIL in phases. Each phase can focus on different aspects of ITIL, allowing for gradual improvement and integration.
5. Adapt ITIL to the Organization
- Customize Frameworks: While ITIL practices are best practices, they may need to be adapted slightly to fit the specific context of your organization.
- Develop Process Documentation: Document all processes, roles, and responsibilities clearly. This documentation will guide the implementation and help maintain consistency.
6. Implement ITIL Processes
- Pilot Test: Start with a pilot project in a critical yet manageable area. Use this as a test case to refine processes before wider implementation.
- Roll Out: Gradually expand the implementation across other areas of IT, constantly adapting the approach based on feedback and results from the pilot.
7. Use Tools and Technology
- Leverage ITSM Tools: Implement IT Service Management tools that support ITIL processes. These tools can help automate workflows, track metrics, and manage documentation.
8. Monitor, Evaluate, and Improve
- Establish Metrics: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of implemented processes.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule regular reviews of the ITIL processes to evaluate success and identify areas for improvement.
- Continual Improvement: Use feedback and performance data to refine and improve ITIL processes continuously.
9. Cultivate a Continual Improvement Culture
- Encourage Feedback: Promote a culture where continuous improvement is valued. Encourage feedback from all stakeholders to foster ongoing optimization of IT service management.
Implementing ITIL is not a one-time project but an ongoing journey. It requires continuous effort, adaptation, and commitment to process improvement. By following these steps, organizations can successfully integrate ITIL practices into their operations, leading to improved IT service management and better alignment with business objectives.